All types of Dropped Ceiling Profiles
Preparation of the text: AZIN ASIA Research Unit of (Azin Asia Holding company)
Dropped ceilings (also known as suspended ceilings or false ceilings) use a variety of profiles that form the framework for supporting ceiling tiles or panels. These profiles are typically made of materials like aluminum, galvanized steel, or PVC, and come in different shapes and sizes depending on the design and structural requirements of the ceiling.
Note : At AZIN ASIA Holding Company, we supply metal profiles for false ceilings and false walls with the best materials.
Below are the key types of profiles used in dropped ceilings:
1. Main Tee (Main Runner)
Function: The Main Tee is the primary profile that runs the length of the ceiling. It provides the main structural support for the dropped ceiling and holds the cross tees in place.
Material: Typically made from galvanized steel or aluminum.
Size: Standard lengths are usually 3.6 meters or 12 feet.
Usage: Installed perpendicular to cross tees to form a grid pattern.
Advantages:
High load-bearing capacity.
Provides the core support for other profiles and ceiling tiles.
2. Cross Tee (Cross Runner)
Function: Cross Tees are secondary profiles that connect to the Main Tee to form a grid pattern. They are spaced at regular intervals and hold the ceiling tiles or panels.
Material: Galvanized steel or aluminum.
Size: Common sizes include 0.6 meters (2 feet) and 1.2 meters (4 feet).
Usage: Fits between Main Tees to create sections for ceiling tiles (typically 2’x2’ or 2’x4’).
Advantages:
Lightweight and easy to install.
Provides flexibility for different tile sizes.
3. Perimeter Angle (Wall Angle or Edge Trim)
Function: The Perimeter Angle or Wall Angle is a "L"-shaped profile that is installed around the perimeter of the room along the walls to support the grid system. It ensures that the edges of the ceiling are neat and stable.
Material: Typically made from steel or aluminum, with PVC options also available.
Size: Standard lengths are 3 meters or 10 feet.
Usage: Attached to the wall to provide a base for the grid system.
Advantages:
Provides a clean finish to the ceiling edges.
Helps secure the grid system to the walls.
4. Suspension Wire or Hanger Wire
Function: Suspension Wire is used to hang the ceiling grid (Main Tees and Cross Tees) from the structural ceiling above. It ensures that the dropped ceiling remains level and stable.
Material: Galvanized steel wire, typically 12 or 14 gauge.
Usage: Wires are attached to the structural ceiling with anchors and looped around the Main Tees to hold the entire system in place.
Advantages:
Provides strong, adjustable support for the ceiling grid.
Allows for height adjustments to ensure a level ceiling.
5. Shadow Moulding
Function: A Shadow Moulding profile is used to create a shadow effect around the perimeter of the dropped ceiling. It enhances the aesthetics by providing a recessed, stylish edge.
Material: Aluminum or steel.
Usage: Installed along the perimeter where the ceiling meets the wall.
Advantages:
Adds a modern, decorative look to the ceiling.
Helps conceal gaps between the ceiling and the wall.
6. Exposed Grid Profiles (T-Bar or T-Grid)
Function: Exposed Grid Profiles are visible once the ceiling is installed. They form the grid system that holds the ceiling tiles in place.
Material: Galvanized steel or aluminum.
Types:
Standard T-Bar: Most common grid used in commercial and residential settings.
Slimline T-Bar: Offers a more minimalistic look with a thinner profile.
Decorative T-Bar: Profiles with finishes like wood or metallic textures for a high-end look.
Usage: Forms the framework for the ceiling, visible between tiles.
Advantages:
Easy to install and adjust.
Can be used with different ceiling tile types.
7. Concealed Grid Profiles
Function: Concealed Grid Profiles are hidden behind the ceiling tiles, providing a clean and seamless ceiling appearance.
Material: Galvanized steel or aluminum.
Usage: Common in spaces where a modern, sleek finish is desired.
Advantages:
Provides a flush, uninterrupted ceiling surface.
Ideal for premium interior designs.
8. Z-Bar Profile
Function: The Z-Bar Profile is a special type of profile used in ceilings where tiles need to be removable or accessible, often for maintenance purposes.
Material: Galvanized steel or aluminum.
Usage: Commonly used in environments where access to the plenum space above the ceiling is needed.
Advantages:
Provides easy access to the space above the ceiling for maintenance or repairs.
Often used in combination with concealed grids.
9. Box Profile
Function: Box Profiles provide extra strength for dropped ceilings, especially in areas that need higher load-bearing capacity (e.g., in industrial settings).
Material: Galvanized steel.
Usage: Supports heavier tiles or elements like lighting fixtures.
Advantages:
Strong and durable, ideal for heavy-duty applications.
Can accommodate heavier materials like gypsum boards or acoustic panels.
10. Clip-in Profile (Hook-on Profile)
Function: Clip-in Profiles are used for clip-in ceiling systems, where tiles are clipped into the framework, creating a smooth and flush surface without exposed gridlines.
Material: Galvanized steel or aluminum.
Usage: Widely used in commercial settings where aesthetic uniformity and easy maintenance are important.
Advantages:
Clean, seamless look with hidden supports.
Easy to remove and replace individual tiles.
11. Omega Profile
Function: The Omega Profile is used for fixing tiles or panels to walls or ceilings in specific architectural designs.
Material: Aluminum or galvanized steel.
Usage: Provides support for lightweight wall or ceiling panels in places like hospitals, offices, or retail spaces.
Advantages:
Versatile and can be used both for walls and ceilings.
Creates strong support for lightweight materials.
12. Furring Channel (Hat Profile)
Function: Furring Channels or Hat Profiles are often used in combination with drywall ceilings or panels. They provide a base for fixing ceiling materials to the grid system.
Material: Galvanized steel.
Usage: Installed across joists to support ceiling boards or drywall.
Advantages:
Strong, corrosion-resistant material.
Lightweight and easy to install.
13. PVC Profiles
Function: PVC Profiles are used for lightweight and moisture-resistant ceiling systems, especially in areas like bathrooms, kitchens, or damp environments.
Material: PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride).
Usage: Offers an alternative to metal profiles in environments that require moisture resistance.
Advantages:
Resistant to moisture and corrosion.
Lightweight and easy to clean.
14. C-Channel Profile
Function: C-Channel Profiles are support structures used in heavy-duty or industrial dropped ceilings where increased strength is required.
Material: Galvanized steel.
Usage: Provides strong structural support for ceilings that bear heavier loads.
Advantages:
High load-bearing capacity.
Durable and long-lasting.
Conclusion
Dropped ceiling profiles come in various types to support different design, aesthetic, and structural needs. From Main Tees and Cross Tees that form the basic grid structure, to Concealed Profiles and Clip-in Profiles for seamless looks, these profiles ensure a flexible and reliable framework for ceiling installation.
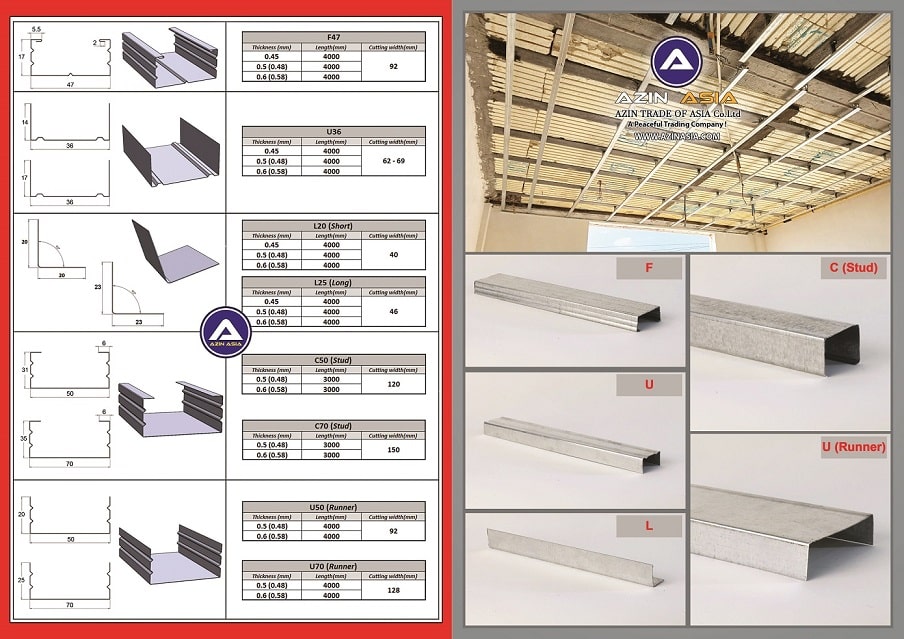
What are F,U,C,L profiles of dropped Ceiling ?
The F, U, C, and L profiles used in dropped ceilings refer to different types of framing profiles based on their shape, which are critical in supporting and securing the ceiling system. These profiles help create the framework for hanging ceiling panels, tiles, or gypsum boards in a suspended ceiling system. Here's a breakdown of each:
1. F Profile (Flange Profile)
Shape: "F" shaped, with a flange that extends outward.
Function: Often used to provide a finishing edge or a border for suspended ceiling panels. It helps create a smooth transition between the wall and the ceiling.
Usage: Installed at the perimeter of the room, where the ceiling meets the walls. It supports the edge of ceiling tiles and gives a clean finish.
Material: Aluminum or galvanized steel.
Advantages:
Provides a neat edge to the ceiling, especially in grid systems.
Enhances the aesthetic by hiding imperfections at the junction between the wall and the ceiling.
2. U Profile (U-Channel)
Shape: "U" shaped, with parallel vertical sides.
Function: U-Channel profiles are typically used as secondary support profiles in dropped ceiling systems. They can also be used to hold the ceiling tiles or panels in place.
Usage: Often used in areas where additional framing is required or in conjunction with furring channels and other support elements in the ceiling grid.
Material: Usually made from aluminum or galvanized steel.
Advantages:
Provides extra structural support.
Used for light partition walls or to create channels for holding tiles or panels in place.
3. C Profile (C-Channel)
Shape: "C" shaped, similar to a U-channel but with a lip or flange at the top and bottom.
Function: The C-Profile is primarily used as a support profile in the grid system. It is also used for drywall installation and heavy-duty ceiling systems that require higher strength.
Usage: Installed in conjunction with other profiles (e.g., U-channels or main tees) to support the weight of heavier ceiling materials, such as gypsum boards or acoustic panels.
Material: Galvanized steel, commonly used for its strength and durability.
Advantages:
High load-bearing capacity.
Ideal for heavy-duty dropped ceiling installations where additional support is needed.
4. L Profile (L-Angle or Wall Angle)
Shape: "L" shaped, with one leg of the "L" attached to the wall and the other extending outward.
Function: L Profiles or Wall Angles are perimeter trims used to support the edges of ceiling tiles or panels. They form the border between the ceiling and the walls, ensuring the grid system is supported along the edges.
Usage: Installed along the perimeter of the room, supporting the grid and providing a clean, finished edge.
Material: Aluminum or galvanized steel.
Advantages:
Helps ensure the ceiling grid is level and properly supported at the edges.
Enhances the overall look by giving a clean, professional finish where the ceiling meets the walls.
Summary of Functions:
F Profile: Finishing edge for the ceiling, often used for neat transitions.
U Profile: Provides extra support in the ceiling grid system, often used for lightweight applications.
C Profile: Heavy-duty support profile for ceilings requiring higher load capacity.
L Profile: Perimeter trim to support the edges of the ceiling and provide a clean, finished look.
These profiles are crucial components in the structural integrity, aesthetic appeal, and overall functionality of dropped ceiling systems.
Dropped Celing Profiles
Dropped ceiling profiles form the structural framework that supports the ceiling tiles or panels. These profiles are typically made of galvanized steel, aluminum, or PVC and are arranged in a grid system to suspend the ceiling below the structural ceiling. Here’s a breakdown of the primary dropped ceiling profiles used in suspended ceiling systems:
1. Main Tee (Main Runner)
Function: The main structural support that runs the length of the ceiling.
Material: Galvanized steel or aluminum.
Length: Typically 3.6 meters (12 feet).
Usage: Installed first in a grid system to carry the weight of the tiles and connect the cross tees.
Advantages:
High load-bearing capacity.
Acts as the core of the suspended ceiling system.
2. Cross Tee (Cross Runner)
Function: Secondary profiles that intersect with the main tees to create the grid that holds the ceiling tiles.
Material: Galvanized steel or aluminum.
Length: Common sizes are 0.6 meters (2 feet) or 1.2 meters (4 feet).
Usage: Connects perpendicular to the main tee, creating squares or rectangles for ceiling tiles (commonly 2’x2’ or 2’x4’).
Advantages:
Easy to install and connect.
Lightweight yet strong.
3. Perimeter Angle (Wall Angle or L Profile)
Function: L-shaped profile that is installed along the perimeter of the room to support the edges of the grid system.
Material: Galvanized steel, aluminum, or PVC.
Usage: Fixed to the wall to secure the outer edges of the dropped ceiling grid system.
Advantages:
Provides a clean and professional edge finish.
Helps secure and stabilize the grid system along the walls.
4. Suspension Wire (Hanger Wire)
Function: Wires used to suspend the ceiling grid (main tees and cross tees) from the structural ceiling.
Material: Galvanized steel.
Gauge: Commonly 12 or 14 gauge.
Usage: Suspended from the ceiling using anchors to support the grid system.
Advantages:
Strong and adjustable, ensuring the ceiling remains level.
Allows height adjustments for the grid.
5. Z-Bar Profile
Function: Used for ceiling systems that require access to the space above for maintenance. The profile allows ceiling tiles to be easily removed and replaced.
Material: Aluminum or galvanized steel.
Usage: Typically used in commercial and industrial settings where access to HVAC, plumbing, or electrical systems is needed.
Advantages:
Provides easy access to the plenum (space above the ceiling).
Ensures that tiles can be easily removed and reinstalled without damaging the system.
6. Furring Channel
Function: A hat-shaped profile used to support ceiling tiles or panels, commonly used for drywall ceilings.
Material: Galvanized steel.
Usage: Installed across joists to support drywall or other ceiling materials.
Advantages:
Lightweight and durable.
Provides a strong framework for attaching ceiling boards or tiles.
7. C-Channel Profile
Function: C-shaped profile that provides strong support for heavier ceiling systems, often used in industrial or commercial installations.
Material: Galvanized steel.
Usage: Used where additional support is needed for heavier ceiling panels like gypsum boards.
Advantages:
High load-bearing capacity.
Durable and corrosion-resistant.
8. Omega Profile
Function: Used to support lightweight panels or ceiling tiles in specific architectural designs.
Material: Galvanized steel or aluminum.
Usage: Commonly used in commercial and residential settings for lightweight partition walls or ceiling systems.
Advantages:
Versatile and provides strong support.
Lightweight and easy to install.
9. Clip-in Profile (Concealed Grid Profile)
Function: Used for concealed ceiling systems where the grid is hidden, creating a smooth and seamless ceiling surface.
Material: Galvanized steel or aluminum.
Usage: In commercial spaces where aesthetic appeal is important, tiles are clipped into the frame.
Advantages:
Provides a clean, seamless appearance.
Easy to install and maintain.
10. Shadow Moulding
Function: Perimeter profile that creates a shadow effect, giving the ceiling a more modern and aesthetic appearance.
Material: Aluminum or steel.
Usage: Installed around the edges of the ceiling to create a recessed look.
Advantages:
Adds a decorative finish.
Provides a modern, sleek look.
11. Exposed Grid Profiles (T-Bar System)
Function: Exposed grid profiles form the visible part of the ceiling system where ceiling tiles are placed. They can come in various styles:
Standard T-Bar: The most common type, visible between ceiling tiles.
Slimline T-Bar: A thinner profile for a more minimalist look.
Material: Aluminum or galvanized steel.
Usage: Used in commercial and residential ceiling installations.
Advantages:
Easy to install and adjust.
Versatile and available in different finishes for aesthetic purposes.
12. Box Profile
Function: Used in ceiling systems that require heavy-duty support, especially in areas with large spans or heavier tiles/panels.
Material: Galvanized steel.
Usage: Provides additional strength for ceilings supporting heavy fixtures.
Advantages:
Strong and durable.
Ideal for industrial or commercial applications.
13. PVC Profiles
Function: Used in areas where moisture resistance is required, such as bathrooms, kitchens, or damp environments.
Material: Polyvinyl chloride (PVC).
Usage: Provides support for lightweight ceiling tiles or panels, particularly in moisture-prone areas.
Advantages:
Lightweight and moisture-resistant.
Easy to clean and maintain.
Summary of Profiles for Dropped Ceilings:
Main Tee & Cross Tee: Primary and secondary profiles that form the grid system.
Perimeter Angle (L Profile): Provides support at the edges of the ceiling.
Suspension Wire: Hangs the grid system from the structural ceiling.
C-Channel, Furring Channel, Omega, Z-Bar: Used for additional support or special purposes.
Clip-in & Exposed Grid: Provide concealed or exposed finishes depending on the ceiling design.
PVC & Box Profiles: Special profiles for moisture-prone or heavy-duty applications.
These profiles form the skeleton of the dropped ceiling system and determine its structural integrity, functionality, and appearance. Each type of profile plays a crucial role in supporting the ceiling and ensuring durability, ease of installation, and aesthetics.
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/all-types-dropped-ceiling-profiles-reza-habibi-zadeh-dogvf
989120896902+
986142288360+
986142288361+




